The standard wire gages are listed below:
Plc Tutorial,Online Plc Tutorial,Plc tutor,Plc Tutorials - This blog contains complete details of PLC Need Live PLC Training logon to: http://tiia.co.in/
Tuesday, April 26, 2011
PLC Wiring
The standard wire gages are listed below:
Monday, April 18, 2011
ALLEN BRADLEY PROGRAMING GUIDE
Then select CPU model
PLC SCAN PROCESS
PLC PROGRAM SCAN
Saturday, April 16, 2011
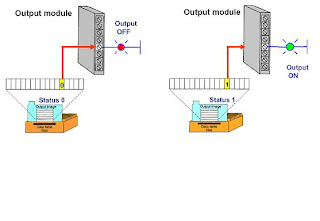
PLC OUTPUT TABLE FILE OPERATION
PLC INPUT TABLE FILE OPERATION:
PLC PROCESSOR MEMORY ORGANIZATION
The memory of a PLC is organized by types.
The memory space can be divided into two broad categories:
Program and Data Memory:
Advanced ladder logic functins allow controllers to perform calculatins, make decisions and do other complex tasks. Timers and counters are examples of ladder logic functions. They are more comples than basic inputs contacts and output coils and relay heavily upon data stored in the memory of the PLC.
The user program will account for most of the memory of a PLC system.
Program files contain the logic controlling machine operation.
This logic consistes of instructions that are programmed in a ladder logic format.
DATA FILES:
The data file protion of memory stores input and output status, processor status, the status of various bits and numerical data.
What is a PLC?
PLC is a device, which is used to control a machine or process as per the human control sequence. A PLC monitors inputs, makes decisions based on its program, and controls outputs to automate a process or machine.
Advantages
• Smaller physical size than hard-wire solutions
• Easier and faster to make changes
• PLCs have integrated diagnostics and override functions
• Diagnostics are centrally available
• Applications can be immediately documented
• Applications can be duplicated faster and less expensively
PLC HARDWIRED CONTROL
Prior to PLCs, many of these control tasks were solved with contactor or relay controls. This is often referred to as hard-wired control. Circuit diagrams had to be designed, electrical components specified and installed, and wiring lists created. Electricians would then wire the components necessary to perform a specific task. If an error was made the wires had to be reconnected correctly. A change in function or system expansion required extensive component changes and rewiring.
DRAWBACKS:
Bulky and complex wiring.
Difficult to change the logic.
Unreliable.
RELAY :

RELAY LOGIC – AND GATE:
Logic gates and Electronic Circuits are used
Ease of programming
Ease of maintenance
Drawbacks:
Difficult to Troubleshoot while Change the Logic of the Process
Difficult to expand
Not suitable for industrial conditions